Chest of osteochondrosis is a chronic disease, in which it is based, specific of the defeat intervertebral cartilage disks, which leads to reactive changes on the part of the vertebral bodies and soft tissues. The disease is widespread and affects mainly people over working age (25-45 years).
Chest of osteochondrosis is considerably less lumbar or cervical. This is because in this department of the spinal column, which represents less static and motor load than others. However, the osteochondrosis of breastfeeding and of the spine is more difficult to diagnose, since in most of the cases they are simulating a disease of the lungs, the heart, the organs of the upper division of the digestive system.
Causes and risk factors
At present, the exact causes of the development of the breastfeeding and osteochondrosis are not installed. Specialists proposed various theories (infectious-allergic, hereditary, manual, hormonal, vascular), but none of them gives a clear and complete explanation pathological changes that occur in the spine and lead to degeneration of the tissues. It is likely that, in patalgico the mechanism of development of breastfeeding and of the osteochondrosis at the same time, participates on several factors. But the main value belongs to the long-static-dynamic-overload-segment spinal.
Factors that cause such overload, are:
- abnormalities of the structure of the spine;
- the asymmetric disposition of joint guidance of the clefts in the intervertebral joints;
- the narrowing of the spinal canal;
- spondylogenic muscle (myofascial, collected) and/or somatic (collected, occur in the context of several diseases of the blood vessels and internal organs) pain;
- prolonged exposure to the spine of the vibration, for example, drivers of motor vehicles;
- physical surge;
- obesity;
- smoking;
- sedentary lifestyle (physical inactivity);
- the psychosocial factors.
The mobility of the spine is obtained by means of the intervertebral discs, which also play and cushioning role. In the centre is an elastic gelatinous core, and in which a large amount of water. The osteochondrosis the nucleus begins to lose water as a result of the demineralization of the polysaccharides. With time, the core of uploshchaetsya, and along with it, uploshchaetsya and the intervertebral disc. Under the influence of the mechanical loading annulus fibrosus bulges, this process is called the protrusion. In the future, in the disc cracks through which the falling fragments of nucleus gelatinous, that is to say, occurs the formation of the hernia of the intervertebral disc.
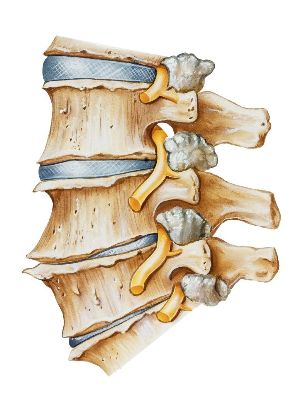
Decrease of the height of the unit leads to a convergence of adjacent vertebrae, the violation of the anatomy of facet joints. All of this initiates the reactive inflammation in the facet joints and soft tissues. In addition, the approach of the bodies of the vertebrae, accompanied by the extension of the joint capsules, and surprised with the segment of the spinal column becomes unstable. The body of the vertebrae to receive an excess of mobility, that may be the cause of the violation of spinal roots and the development of a syndrome of the root.
In the background of breastfeeding and of the osteochondrosis gradually expands the bone tissue of the bodies of the vertebrae, and bony growths (osteophytes). Can also be the cause of the syndrome, radicular or myelopathy compression (sdavleniya of the spinal cord).
Classification
On the basis of the clinical classification of osteochondrosis est posindromnoy principle. Depending on which nerve of education affected by the structure of the spine affect, are distinguished the following syndromes:
- features – basis of our development lies the tension, the deformation or compression of the nerve root, the phase of the spinal cord or a blood vessel, in function of which develop medullary, cardiovascular disease, or root of the syndromes;
- reflector associated with reflex tension of innervated muscle, degenerative and vascular of the disability;
- bioadaptive.
The symptoms of breastfeeding and of osteochondrosis
The main symptom of breast-feeding, and of the osteochondrosis is pain. In most cases, she is clumsy, mildly.
Much irritation of the spinal roots becomes the cause of disorders of the innervation of the internal organs. Depending on the level of the defeat, the chest of the osteochondrosis can flow under the mask of pathologies, somatic:
| The level of defeat | Innervated organ | The clinical symptoms of the |
| C7-Th1 | Of the hand, the wrist, the palm, the trachea, the esophagus | Pain in the arms and the palms of the hands, bronchial asthma |
| Ap2-Th3 | The heart, pericardium, coronary artery | Coronary heart disease, arrhythmias, |
| Rh4-Rh5 | The bronchi, lungs, pleura, breasts, nipples, | Bronchitis, pneumonia, pleural effusion>[!@#$], bronchial asthma |
| Th5-Th6 | Common bile duct, the gallbladder | The gallstone disease, the violation of a process of assimilation of fats |
| Th6-Th7 | The liver, the solar plexus | Failure of the liver function |
| Th7-Th8 | The stomach | Dyspepsia, gastritis, ulcer of stomach and duodenum |
| Th8-Th9 | Duodenum, pancreas | Disorders of digestion and of the chair, duodenitis, pancreatitis |
| Th9-Th10 | The spleen, diaphragm | Hiccups respiratory, of the violation of |
| Th10-Th11 | The adrenal glands | Allergic reactions, decrease immunity |
| Th11-Th12 | The kidneys | The pyelonephritis, urolithiasis |
| Th12-L1 | The kidneys and ureters | Violation of urination |
In this sense, the most frequent clinical symptoms of degenerative disc disease are:
- pain in the chest (on the sternum, on the side, the back, intercostal medium) – can be acute, and the pain, clumsy; often radiates to the sugar arm;
- pain in the area of epigastrium – arise regardless of the nature of foods, the characteristics of the diet, often combined with acid reflux, nausea, vomiting;
- pain in the area of the right hypochondrium – are intensified when you change the position of the patient's body, sneezing, cough;
- the pain in the lumbar area – simulate an attack of renal colic, often combined with dysuric disorders.
With the compression of the nerve root in the patient's native osteochondrosis develops the attack of intercostal neuralgia. For him characterized by the appearance of acute pain in one half of the rib cage (torakalgiya). Painful sensations are ringworm of the nature and are distributed by the departure of one of the intercostal nerves from the spine to sternum. Patients describe it as "a stroke of electric current" or "center". The pain can give in the area of the epigastrium, area retrosternal, a spatula, a hand, and combined with some other symptoms (local hyperhidrosis, pallor or congestion of the skin), related to the defeat of the sympathetic fibers intercostal nerve.
For intercostal neuralgia are characteristic paroxysms of pain, lasting from few seconds to several minutes. During an attack of pain become intolerable. Trying to somehow alleviate their condition, the patients is reassuring in a certain position of the body, avoiding deep, cough, sneeze, spin.
Out of pain of an attack of the patients observed paresthesia (subjective of the violation of the sensitivity of the skin in the form of the crawling chills, tickling, tingling, pin) during intercostal space.
The diagnosis
The diagnosis of breastfeeding and of the osteochondrosis conducted on the basis of data, objective of the inspection of the patient, laboratory and instrumental survey, which includes:
- the general analysis of blood-moderate leukocytosis, increase of esr);
- the serum electrolytes of the blood (decreased calcium levels);
- analysis of urine;
- biochemical analysis of the blood;
- the chest x-ray of the spine (is detected, the flattening of the intervertebral disc, the deformation occupy the last positions of the disks of the vertebral bodies adjacent to, the displacement of the vertebral bodies adjacent with respect to the other);
- scan of the spine (identifies the active process of bone mineralization of the vertebral bodies);
- myelography;
- computer and magnetic resonance tomography.
Chest of osteochondrosis requires a differential diagnosis with the diseases and pathological states:
- dishormonal spondylopathy;
- spondylolisthesis;
- inflammatory processes;
- ankylosing spondylitis;
- osteomyelitis of the spine;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- neoplastic processes of metastasis or primary tumor of the rib cage);
- fractures of the spine;
- disease of the intestinal tract (chronic pancreatitis, ulcer of stomach and duodenum, diverticulitis, irritable bowel syndrome);
- diseases of the genitourinary system (urolithiasis, pyelonephritis);
- cardiovascular disease (coronary artery disease, arrhythmias).
The treatment of the osteochondrosis of breastfeeding and
The treatment of breastfeeding and the osteochondrosis is carried out on an outpatient basis. When expressed syndrome painful in the patient in 2-3 days is prescribed bed rest. It shows the traction affected segment of the spine, which allows to correct the compression of the nerve root and therefore cut off the pain syndrome. When expressed syndrome painful to spend the infiltration of the soft tissues of the 2% by the novocana. A short course can be designated nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents.
In the scheme of comprehensive treatment, of breastfeeding and of the osteochondrosis also include:
- antihistamines;
- vitamins of the group;
- tranquilizers;
- iglorefleksoterapija;
- massage;
- the practice of chiropractic.
After improving the state of the patient is sent to the most important classes of physical culture medicinal. The implementation of regular exercise a physical when the osteochondrosis that promotes the formation of well-developed muscular corset, which allows you to keep the spine in the correct physiological position, removes excess static charge.
Of great importance in the treatment of breastfeeding and of the osteochondrosis relegated to regular moderate physical activity (swimming, yoga, tai-chi), the normalization of the mass of the body. Jumping, running, weight lifting and other sports, with higher loads on the spinal column, are contraindicated.
The surgical treatment of breast-feeding, and of the osteochondrosis is shown only in the case of large sdavleniya of the spinal cord. In such cases, depending on the indication they are:
- stabilizing the vertebral segment.
- replacement of the affected unit artificial implant;
- laser reconstruction of the disk drive.
- the puncture of vaporization affected the disk drive.
- microdiskectomy.
The potential consequences and complications
Much irritation or compression of the nerve root can lead to the development of organic diseases of the organs of the ribcage, the upper division of the digestive system, the kidneys. The greatest danger of chest of osteochondrosis is of myocardial.
Also the consequences of breastfeeding and the osteochondrosis can develop in diseases of the esophagus, stomach, duodenum, pancreas, gall bladder, lung, the formation of intervertebral hernia.
Prognosis
Chest of osteochondrosis is characterized by the undulating current, in which the remission accompanied by the acute episodes. When timely had started the treatment, the compliance of a patient of all recommendations of your doctor about how the therapy of the disease and the lifestyle changes, the prognosis is favorable.
The prevention of the
The prevention of breastfeeding and of the osteochondrosis includes:
- the normalization of the mass of the body;
- to stop smoking;
- an active life style.
































